How the iPhone Could Reboot Education

How do you educate a generation of students eternally distracted by the internet, cellphones and video games?Its easy. You enable them by handing out free iPhones — and then integrating the gadget into your curriculum.
That’s the idea Abilene Christian University has to refresh classroom learning. Located in Texas, the private university just finished its first year of a pilot program, in which 1,000 freshman students had the choice between a free iPhone or an iPod Touch.
The initiative’s goal was to explore how the always-connected iPhone might revolutionize the classroom experience with a dash of digital interactivity. Think web apps to turn in homework, look up campus maps, watch lecture podcasts and check class schedules and grades. For classroom participation, there’s even polling software for Abilene students to digitally raise their hand.
The verdict? It’s working quite well. 2,100 Abilene students, or 48 percent of the population, are now equipped with a free iPhone. Fully 97 percent of the faculty population has iPhones too. The iPhone is aiding Abilene in giving students the information they need — when they want it, wherever they want it, said Bill Rankin, a professor of medieval studies who helped plan the initiative.
“It’s kind of the TiVoing of education,” Rankin said in a phone interview. “I watch it when I need it and in ways that I need it. And that makes a huge difference.”
The traditional classroom, where an instructor assigns a textbook, is heading toward obsolescence. Why listen to a single source talk about a printed textbook that will inevitably be outdated in a few years? That setting seems stale and hopelessly limited when pitted against the internet, which opens a portal to a live stream of information provided by billions of minds.“About five years ago my students stopped taking notes,” Rankin said. “I asked, ‘Why are you not taking notes?’ And they said, ‘Why would we take notes on that?…. I can go to Wikipedia or go to Google, and I can get all the information I need.”
Conversely, the problem with the internet is there’s too much information, and it’s difficult to determine which data is valuable.These are the specific educational problems Abilene is targeting with the iPhone. Instead of standing in front of a classroom and talking for an hour, Rankin instructs his students to use their iPhones to look up relevant information on the fly. Then, the students can discuss the information they’ve found, and Rankin leads the dialogue by helping assess which sources are accurate and useful.
It’s like a mashup of a 1960s teach-in with smartphone technology from the 2000s.
Each participating Abilene instructor is incorporating the iPhone differently into their curriculum. In some classrooms, professors project discussion questions onscreen in a PowerPoint presentation. Then, using polling software that Abilene coded for the iPhone, students can answer the questions anonymously by sending responses electronically with their iPhones. The software can also quickly quiz students to gauge whether they’re understanding the lesson.
“Polling opens up new realms for people for discussion,” said Tyler Sutphen, an ACU sophomore who has participated in the iPhone initiative for a year. “It’s a lot more interactive for those who aren’t as willing to jump up and throw out their answer in class. Instead, you push a button on the iPhone.”
Read More http://www.wired.com/gadgetlab/2009/12/iphone-university-abilene/#ixzz0ex07GiiC
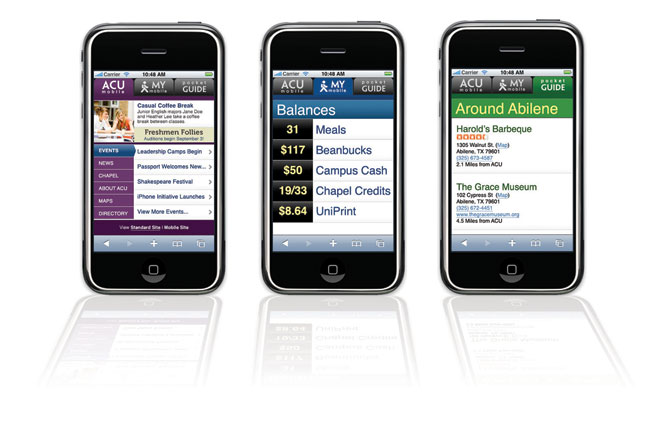
Kasey Stratton, a first-year ACU business student, said her favorite aspect of the iPhone program was how apps are changing the way students interact socially. Many Abilene students use Bump, a free app downloadable through the App Store [iTunes], which enables them to swap e-mails and phone numbers by bumping their iPhones together. Also, the campus’ map app helped her become familiar with the campus quickly when she arrived.
“At ACU it’s like they see [the iPhone] is the way of the future and they might as well take advantage of it,” Stratton said in a phone interview. “They’re preparing us for the real world — not a place where you’re not allowed to use anything.”
Implementing the iPhone program wasn’t easy. In addition to writing custom web apps for the iPhone, the university optimized its campuswide Wi-Fi to support the 2,100 iPhones. Rankin declined to disclose exact figures for money invested in the iPhone program, but he said the initiative only takes up about 1 percent of the university’s annual budget. To offset costs, the university discontinued in-dorm computer labs, since the vast majority of students already own notebooks. Students who opted for iPhones are responsible for paying their own monthly plans with AT&T.
After a successful run, the university plans to continue the iPhone program, with plans to upgrade to new iPhones every two years. Rankin said some UK universities plan to launch similar initiatives as well. In the United States, Stanford doesn’t hand out free iPhones to its students (yet), but it offers an iPhone app called iStanford for students to look up class schedules, the Stanford directory, the campus map and sports news. Stanford also offers a computer science course on iPhone app programming, whose lectures are streamed for free via iTunes.
“For us, it isn’t primarily about the device,” Rankin said. “This is a question of, how do we live and learn in the 21st century now that we have these sorts of connections?…. I think this is the next platform for education.”
