How Google works-
Today we all live and work in the Internet Century, where technology is roiling the business landscape, and the pace of change is only accelerating. In an era when everything is speeding up, the best way for businesses to succeed is to attract smart-creative people and give them an environment where they can thrive at scale. How Google Works is a new book that explains how to do just that.
How Google Works- Know Anything And Everything.
Google uses automated programs called spiders or crawlers, just like most search engines. Also like other search engines, Google has a large index of keywords and where those words can be found. What sets Google apart is how it ranks search results, which in turn determines the order Google displays results on its search engine results page (SERP).
Google Query Box-
A search box, search field or search bar is a graphical control element used in computer programs, such as file managers or web browsers, and on web sites. A search box is usually a single-line text box or search icon with the dedicated function of accepting user input to be searched for in a database.
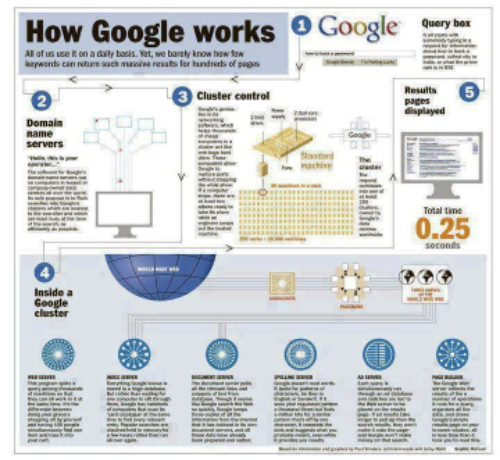
Domain Name Servers, in How google works.
The Domain Name System is a hierarchical and decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other resources connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities.
The process of DNS resolution involves converting a hostname (such as www.example.com) into a computer-friendly IP address (such as 192.168.1.1). An IP address is given to each device on the Internet, and that address is necessary to find the appropriate Internet device – like a street address is used to find a particular home.
When a user wants to load a webpage, a translation must occur between what a user types into their web browser (example.com) and the machine-friendly address necessary to locate the example.com webpage.
In order to understand the process behind the DNS resolution, it’s important to learn about the different hardware components a DNS query must pass between. For the web browser, the DNS lookup occurs “ behind the scenes” and requires no interaction from the user’s computer apart from the initial request.
Cluster Controls-
ClusterControl is a database management tool used to deploy, monitor and scale database clusters. The easy to use web graphical interface to manage, monitor and auto-
scale clustered databases supports MySQL Replication, MySQL Cluster and Galera Cluster.
The core components consist of a controller and one or more agents that are installed on the managed nodes. Each agent reports monitoring data to the controller, which stores the data in a local database.
ClusterControl supports multiple clustering topologies using MySQL Replication, MySQL Cluster and Galera Cluster.
How Google works with SERP?
SERP is an acronym that stands for “Search Engine Results Page”. For anyone working in search engine optimization or PPC, this page on the web is viewed as pristine property — the higher your company ranks, the more exposure and credibility your company will have in regards to search engines.
Google’s first job is to ‘crawl’ the web with ‘spiders.’ These are little-automated programs or bots that scour the net for any and all new information.The Spider will take notes on your website, from the titles you use to the text on each page to learn more about who you are, what you do, and who might be interested in finding you.
So the first massive challenge is to locate new data, record what it’s about, and then store that information (with some accuracy) in a database.
Google’s next job is to figure out how to best match and display the information in its database when someone types in a search query. Scaling becomes a problem again.
Search Engine Steps in How google works.
- Web Crawling
- Indexing
- Algorithms
Web Crawling
This is the means by which search engines can find out what is published out on the World Wide Web. Essentially, crawling is copying what is on web pages and repeatedly checking the multitude of pages to see if they are changed and make a copy of any changes found.
The programs which have the job of doing this are variously referred to as robots, crawlers, spiders or some variation using ‘web’. e.g. web crawler..
Indexing
Once a spider has crawled a web page, the copy that is made is returned to the search engine and stored in a data center.Data centers are huge, purpose built collections of servers which act as a repository of the all the copies of webpages being made by the crawlers.
Google owns dozens of them dotted around the world, which it guards very closely and which are among the most hi-tech buildings in the world.The repository of web pages is referred to as the ‘Index’, and it is this data store which is organized and used to provide the search results you see on the search engine. Indexing is the process of organizing the masses of data and pages so they can be searched quickly for relevant results to your search query.
The Algorithm
Finally, we have a huge collection of web page copies which are being constantly updated and organized so we can quickly find what you are looking for. But we need a means by which they can be ranked in order of relevance to your search term — this is where the Algorithm comes into play.
We don’t know what the algorithm actually is, because search engines tend to keep this a closely guarded secret from competitors and from people looking to game the search engine to get to the top spots. That said, enough about the algorithm has been worked out to let SEOs advise website owners on how to improve their sites and SEO factors to move up in the rankings.
As mentioned above, the title of each webpage has two jobs: ranking and clicking. The title helps with your webpage rankings when it uses a relevant keyword, and it helps with click-throughs when it tells a searcher, “Yes, this page has what you’re looking for.”
When it comes to choosing the text to display on your webpage, Google treats titles in a fairly straightforward way. In general, Google will use the title that you provide, except in certain circumstances such as when the title is missing, poorly written, or very long.
The better the title, the more likely it is that Google will use it and that searchers will like it. To write better titles that Google will approve of, follow these best practices:
- Use a unique title for each webpage.
- Write your title to read well and to describe the content it is linked to.
- Make sure your title is relevant to the content on the webpage.
- Do not stuff keywords into your title.
- Do not use boilerplate titles on your webpages, only changing one or two words.
When you’re writing it, remember that your title has two jobs: to help with your search rankings (because it is considered by the Google search algorithm), but perhaps more importantly, to help your webpage get the click-throughs on the search results page, which in turn helps your SEO.
Hope this article, How Google Works was helpful to you. do you have any further questions?
Ask us in comments below.
for more information you may visit-
- Discover how goggle works by Google
- How Google actually works by Neil Patel
- How google search works: In 3 steps by India Today
To know more about our Managing Director visit him at